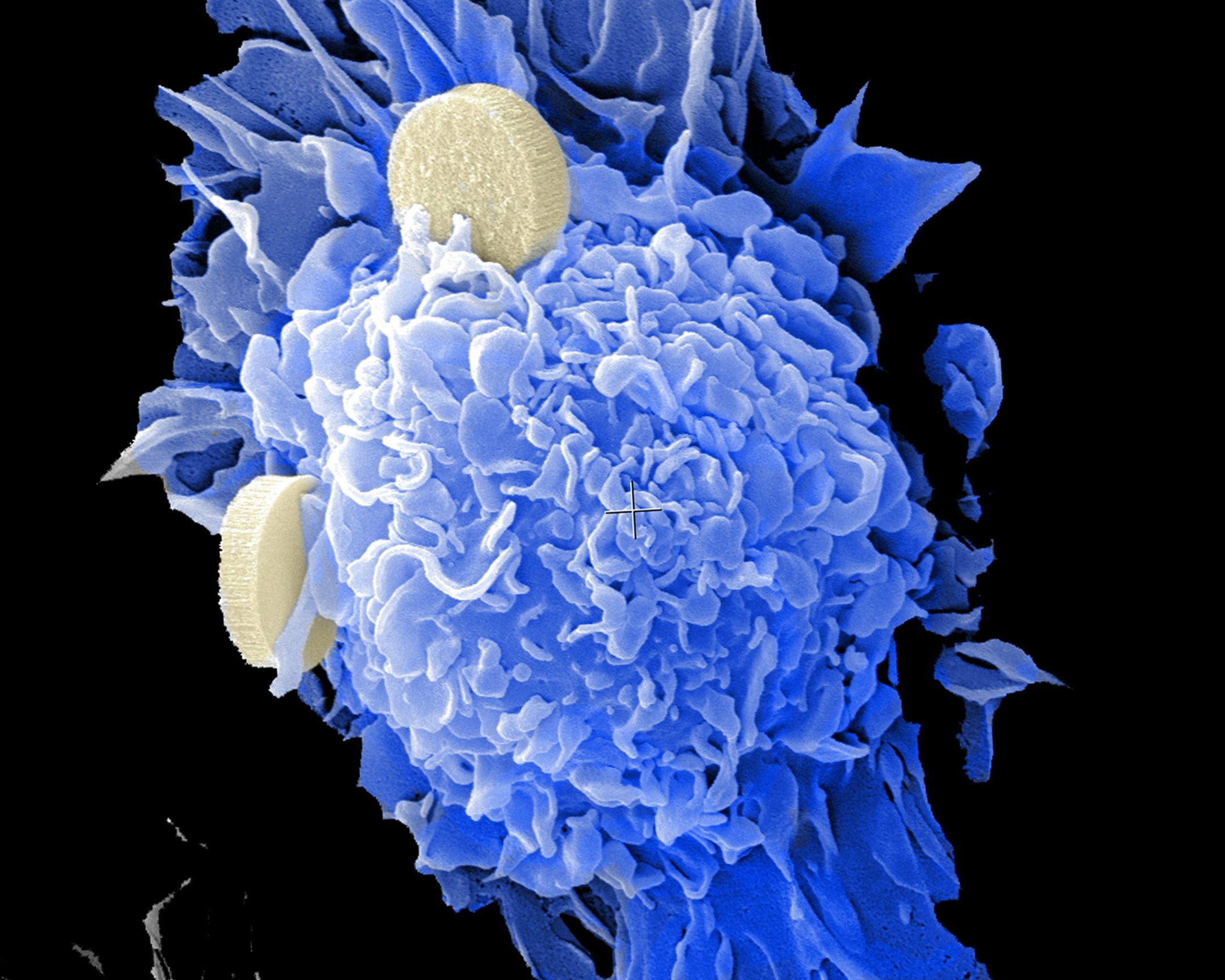
Quantum Computing for Photon-Drug Interactions in Cancer Prevention and Treatment
Using quantum simulation and the power of quantum computers to rationalize optimal drugs for photodynamic cancer therapy.
Owner
Quantum Approach

Quantum Simulation
SDGs
Contributors
Origins of Contributors
lgorithmiq
Cleveland Clinic
IBM

How quantum could help
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a promising cancer treatment that uses light-activated photosensitisers, but designing new drugs for this requires modeling complex excited-state processes, which is a known computationally intensive task and which classical computing falls short of. Quantum simulation could be used in a fully integrated quantum–classical pipeline for excited-state simulations and to identify key challenges in modelling clinically relevant compounds such as TLD-1433—a ruthenium-based PDT drug currently in clinical trials. Research has enabled quantum computers to be initialised in states with high overlap to desired reference states, a longstanding bottleneck in quantum chemistry, and an improvement which also extends well beyond PDT applications. Thus tackling these issues with quantum simulation would address a fundamental challenge within PDT.
