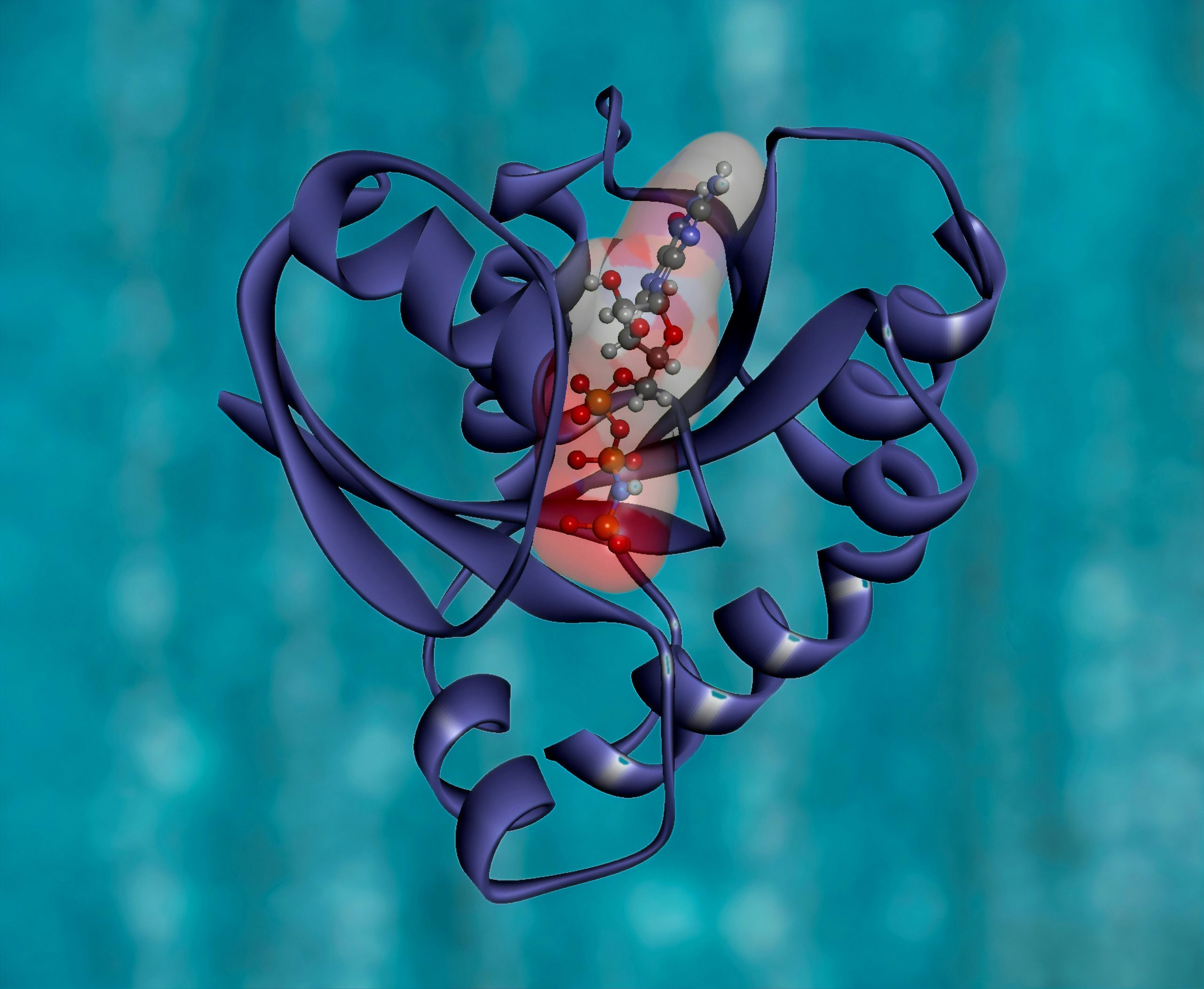

Quantum Computing for hydrolysis reactions in protein environments
Quantum simulation for hydrolysis reactions in protein environments, with a particular focus on adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and guanosine triphosphate (GTP).
Owner
Quantum Approach

Quantum Simulation
SDGs
Contributors
Origins of Contributors
Stanford University
Virginia Tech
Brown University
University of Colorado Boulder
Michigan State University
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
Azulene Labs
NASA
University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign
RIACS
New York University

How quantum could help
ATP and GTP are main metabolic reactions that drive cellular function, where metabolic dysfunction is a key determinant of disease, including many cancers. A detailed understanding of how proteins catalyze the hydrolysis of these reactions could aid the design of new inhibitors and therapeutic strategies. In this case an adaptive variational quantum eigensolver (VQE) could be used to construct force fields capable of driving quantum-mechanically accurate dynamical simulations. These results will guide the development of molecular dynamics models of hydrolysis, ultimately enabling the exploration of fundamental questions surrounding one of the most important chemical reactions in human biology.
